1) Console port, Aux port, Managment port.
https://ipwithease.com/difference-between-console-port-and-management-port-in-networking-devices/
Console: Not have IP address, can see boot seq
Managment: will have IP address, boot seq can not be seen
A benefit of out-of-band management is if you screw up the network somehow, where you might lose connection to the switch if connecting via an in-band method, you continue to be able to manage the device.
When a router sends an RA with ‘O’ bit set, but does not set the ‘M’ bit, the client can do Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) to obtain its IPv6 address, and use DHCPv6 for obtaining additional information. (An example of additional information is DNS). This mechanism is well known as Stateless DHCPv6, because the DHCPv6 server does not need to keep track of the client address bindings.
https://ipwithease.com/difference-between-console-port-and-management-port-in-networking-devices/
Console: Not have IP address, can see boot seq
Managment: will have IP address, boot seq can not be seen
A benefit of out-of-band management is if you screw up the network somehow, where you might lose connection to the switch if connecting via an in-band method, you continue to be able to manage the device.
From Cisco Document :
"
The router includes an asynchronous serial console port and an
auxiliary port. The console and auxiliary ports provide access to the
router either locally using a console terminal connected to the console
port, or remotely using a modem connected to the auxiliary port.
The main difference between the console and auxiliary ports
is that the auxiliary port supports hardware flow control and the
console port does not. Flow control paces the transmission of data
between a sending device and a receiving device. Flow control ensures
that the receiving device can absorb the data sent to it before the
sending device sends more. When the buffers on the receiving device are
full, a message is sent to the sending device to suspend transmission
until the data in the buffers has been processed. Because the auxiliary
port supports flow control, it is ideally suited for use with the
high-speed transmissions of a modem. Console terminals send data at
slower speeds than modems; therefore, the console port is ideally suited
for use with console terminals. "
out-of-band management
involves the use of a dedicated circuit for managing network nodes.
this means that data traffic and mangement traffic do not share the same
circuit. in case of out-of-bound management, traffic flows within a
network on which no production traffic resides.
in-band management means traffic
flows across the enterprise production network or the internet ( or
both). date traffic and mangement traffic share the same channel
ND RA:
=====
https://community.arubanetworks.com/blogs/sumesh-murali1/2020/10/20/explain-the-m-and-o-bit-in-ipv6-dhcp-server-configuration-what-are-the-associated-flags
• ‘M’ bit - "Managed address configuration" flag. When set, it indicates that the client may use DHCPv6 to retrieve a Managed IPv6 address from a DHCPv6 server. If the M flag is set, the O flag is
redundant and can be ignored because DHCPv6 will return all available configuration information.
redundant and can be ignored because DHCPv6 will return all available configuration information.
• ‘O’ bit - "Other
configuration" flag. When set , indicates that other configuration
information is available via DHCPv6. Examples of such information are
DNS-related information or information on other servers within the
network.
When a router sends an RA with ‘O’ bit set, but does not set the ‘M’ bit, the client can do Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) to obtain its IPv6 address, and use DHCPv6 for obtaining additional information. (An example of additional information is DNS). This mechanism is well known as Stateless DHCPv6, because the DHCPv6 server does not need to keep track of the client address bindings.
Note: If neither M nor O flags are set, this indicates that no information is available via DHCPv6.
IP Cisco:
https://ipcisco.com/lesson/ipv6-ndp-neighbour-discovery-protocol/
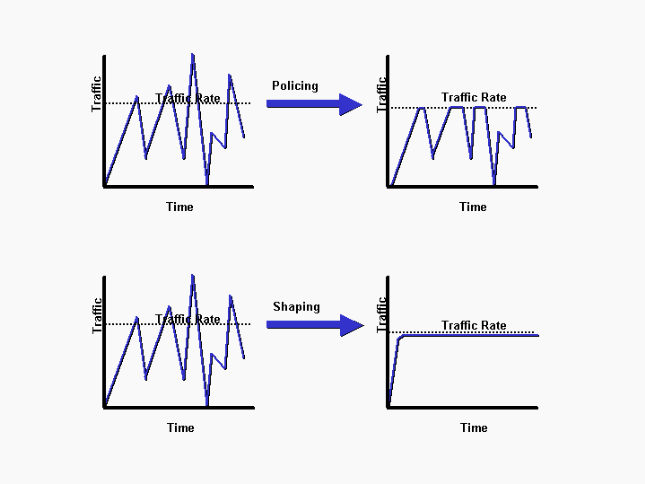
Shaping & Policing:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/quality-of-service-qos/qos-policing/19645-policevsshape.html
ingress(Traffic from hardware to end device/CPE)/down link traffic:
egress (Traffic from CPE to Hardware)/UP link traffic:

only egress/downlink traffic will have shapping/queing.
ingress/uplink traffic will not have shappers. only policying will be there.
usually: Ingress---->Policers
Egress--->Shappers
ND: